Members of Sublinear Data Structure Group
| Name | Affiliation | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Tetsuo Shibuya | University of Tokyo | Groupe Leader |
| Taku Onodera | Univrsity of Tokyo | Member |
| Dong Gyu Lee | University of Tokyo | Member |
| Yang Li | University of Tokyo | Research Assistant |
| Kunihiko Sadakane | University of Tokyo | Member |
| Shuhei Denzumi | University of Tokyo | Member |
| Taito Lee | University of Tokyo | Research Assistant |
| Masayuki Takeda | Kyushu University | Member |
| Hiroshi Sakamoto | Kyushu Institute of Technology | Member |
| Yoshimasa Takabatake | Kyushu Institute of Technology | Research Assistant |
| Tokio Sakamoto | Kyushu Institute of Technology | Research Assistant |
| Shin-ichi Tanigawa | Kyoto University | Member |
| Shin-ichi Nakano | Gunma University | Member |
| Katsutoshi Yada | Kansai University | Member |
| Takuya Kida | Hokkaido University | Member |
| Takuya Masaki | Hokkaido University | Research Assistant |
Research Theme: Sublinear Data Structre Paradigm for Big Data
 In the big data era, various data increases with much faster speed than the Moore's law. It means that algorithms that runs in linear time, or those that requires linear space cannot be applied against such big data in the near future. Our group aims for developing new paradigm for data structures that can be processed in sublinear time and/or space.
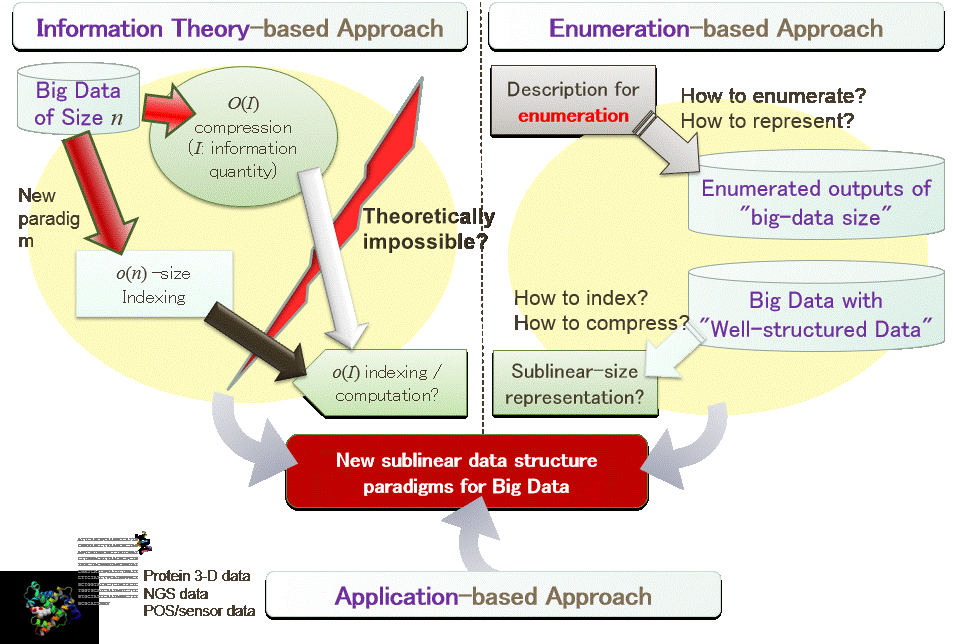
In the big data era, various data increases with much faster speed than the Moore's law. It means that algorithms that runs in linear time, or those that requires linear space cannot be applied against such big data in the near future. Our group aims for developing new paradigm for data structures that can be processed in sublinear time and/or space. All the big data are collected with some objectives, which means that they are not random. It also means that they do not contain so much information in it, in relative to their size. In this sense, we assume that most big data should have some "sublinear data structures" that represent their essential contents while they can be processed efficiently. In this group, we aim for building a new scheme of "sublinear data structures" for such big data processing, by the following three approaches.
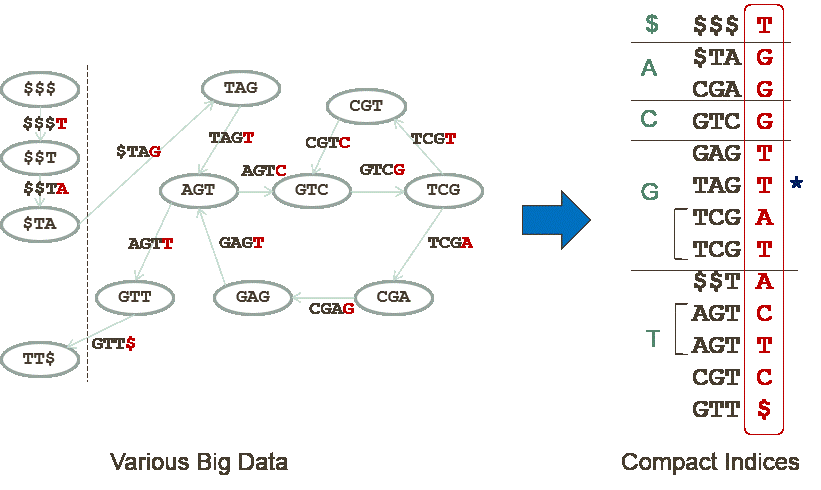
- Information-based Approach In the first approach, we consider the information quantity of the big data. Big data could be compressed to the size of information quantity, permitting efficient searching or any other processing. It could improve also the I/O complexity or communication complexity of algorithms. It could also improve the efficiency of GPGPU with small memory. Moreover, not all the information is required for processing big data, which means that we could break the barrier of information quantity barrier in some of the applications. We aim for developing a new paradigm of compressed data structures for various fundamental data.
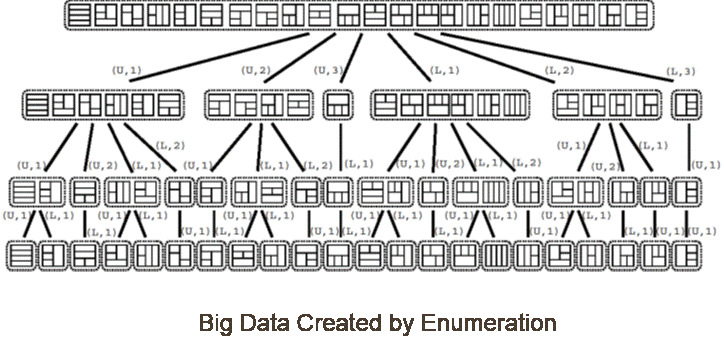
- Enumeration-based Approach In the second approach, we aim for developing a new data structure paradigm based on enumeration algorithms, considering that enumeration algorithms can yield gigantic-size data from a very small information. We assume that some types of big data should have properties similar to the enumerated objects by such enumeration algorithms, and the enumeration algorithms could help development of new sublinear data structure paradigm.
- Application-based Approach In the third approach, we aim for developing sublinear data structures for various real big data, such as DNA data, protein structure data, and POS/sensor data at stores. Through these development, we aim for finding the common data structure paradigm among these researches on these real big data.